Anglais 4e
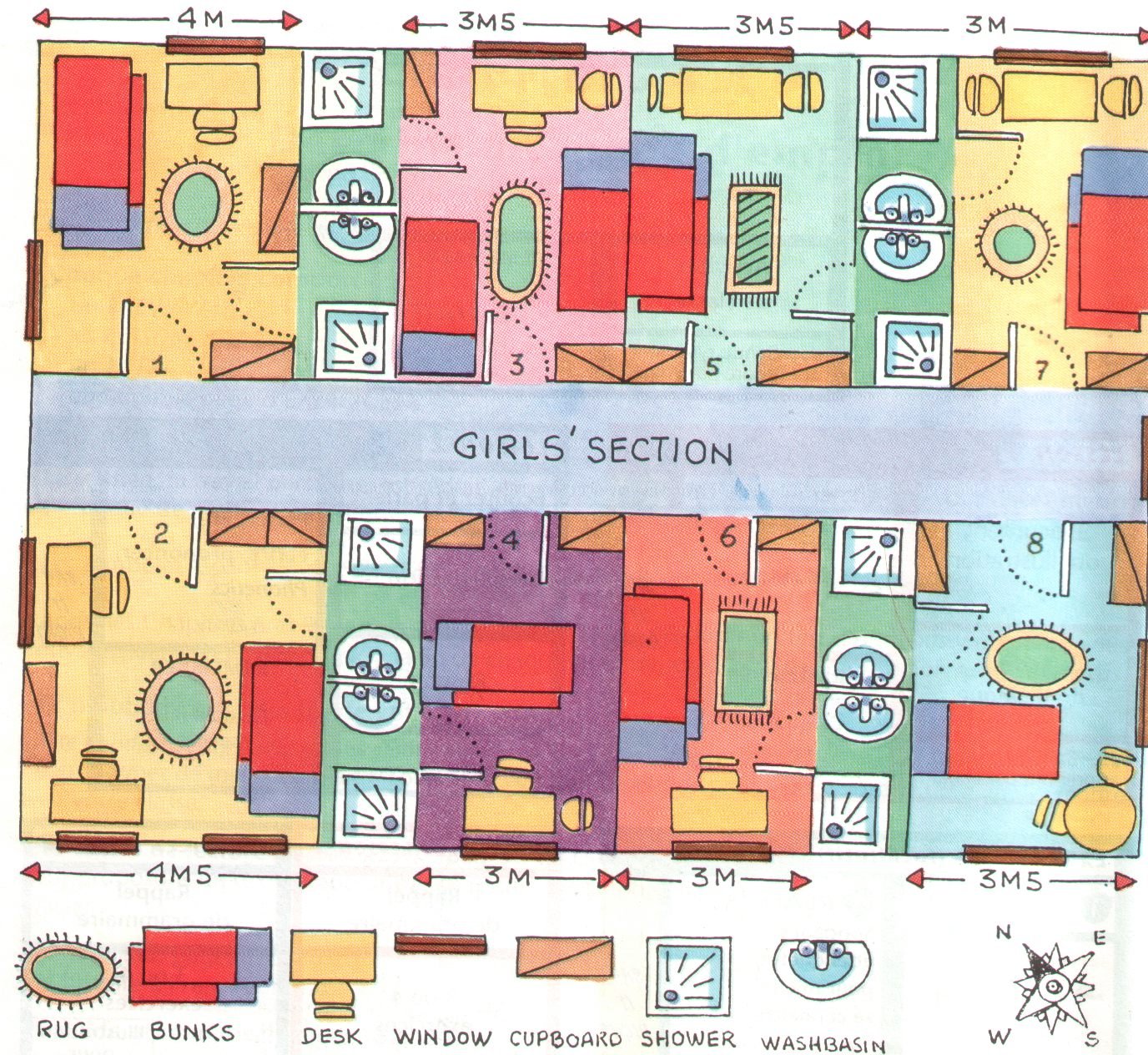
Adventure International


- Adventure international is a holiday camp
- It is in Bude ( town ), Cornwall ( country ),
England ( country )
- Gladys Taylor is the camp supervisor
- Liz and jack are the sport instructors
- The camp is near the sea
Welcome to adventure international
!
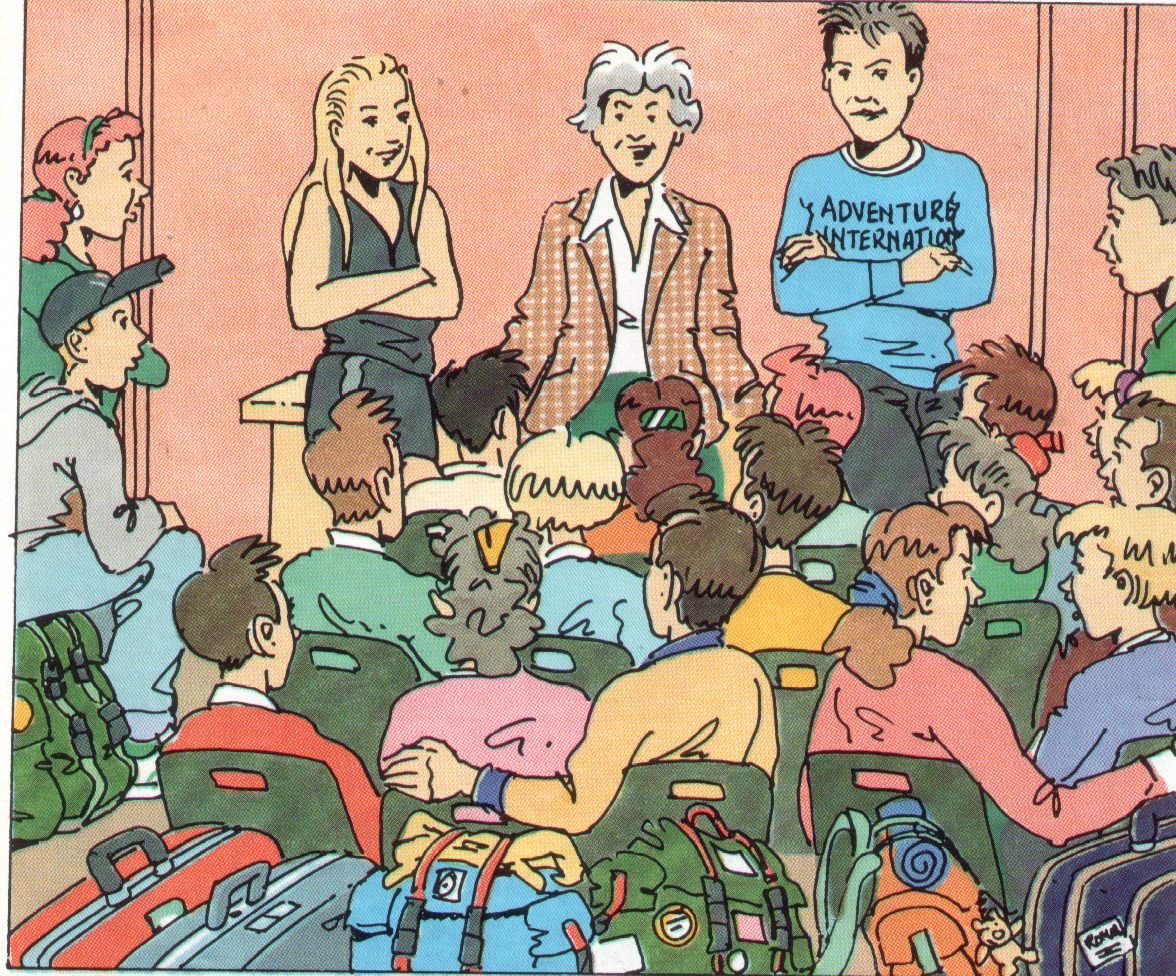

- Gladys Taylor is a nurse
- She looks after ( surveiller ) the children
- Jack May is not married, but he engaged = fiancé
- Liz Moore is engaged too
- Her nickname is " Butterfly " because she swims the
200m butterfly
- She is training for the olympic Games = she is a champion
Similarities :
- Liz is engaged and so is jack
- Jordane has got a sister and so has Maxime
- Liz swims very well and so does Jack
- He went to bude yesterday and so did I
- He at school and so where my two sisters
Deb and Paul
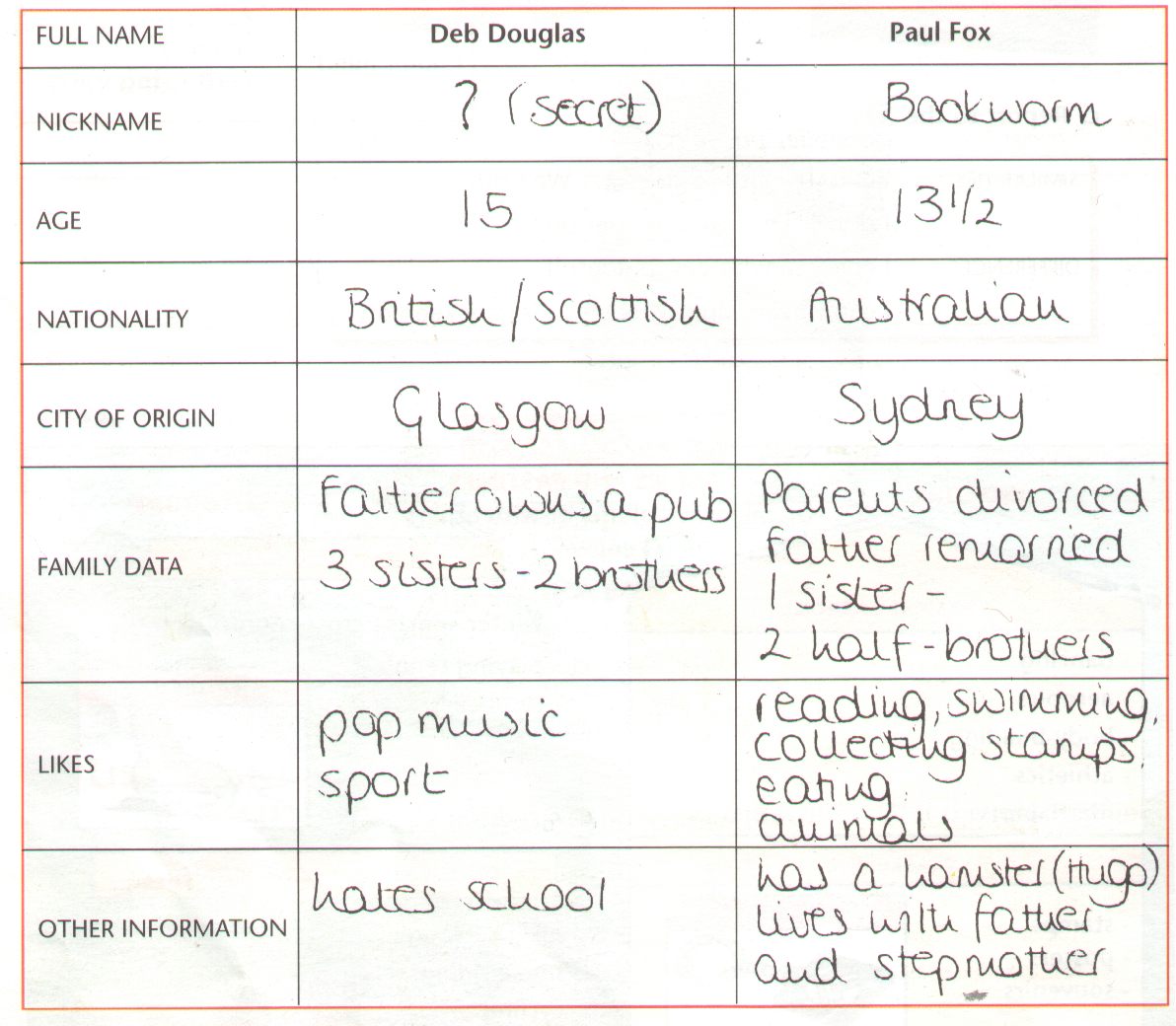
- Deb is from Scotland ----> She is scottish
- her father owns a pub = possède un café
- her nickname is a secret
- Paul is from Sidney ----> He is Australian
- He lives with his father and his step mother ( his
dad is re-married )
- His nickname is " Bookworm " because he loves reading
- Walter is from the States. He hasn't got any brothers
and sisters = he is an only child

- Expressions
- I like = I love = I enjoy = I am fond of = I am interested
in = I am keen on + nom + ing
- I hate = I destest = I can't stand = I cant't bear + nom +
ing
- Similarities : moi non
plus
- I dont like rugby neither do I
- I can't stand hiking Neither can I
|
Exercice
Similarities
He is working and so am I
I'm tired and so are they
You are good at Maths and so is your
friend
My sister isn't tall and neither is my brother
You haven'tgot a moped and neither have
I
Walter likes baseball and so does Paul
I don't enjoy hiking and neither do you
My parents hate skiing and so do I
I was at school yesterday and so were
you
The teacher wasn't absent and neither was
I
Liz trained for 2 hours and so did Jack
We went to Bude last week and so did
Gladys
I can't draw very well and neither can
you
She didn't take a taxi and neither did
I
|
Wilma is absent-minded !

Verbs :
to miss : manquer, rater
to carry : porter, transporter
to wear : porter un vêtement
Vocabulary :
sunglasses : lunettes de soleil
a backpack : un sac a dos
Adjectives :
Wilma is absent - minded : étourdies, distraite, tête
en l'air
lovely = nice : adorable
anxious > worried
Don't worry ----> Ne t'inquiète pas !
pleased = happy : contente
sad : miserable
Question sur la description physique :
What does Wilma look like ? ----> She is tall
Question sur le caractère
What is Wilma like ? ----> She is absent
- minded

Les adjectifs composés :
a curly-ahired boy
a blue-eyed boy
a left-ganded boy
Mes cheveux :
I am a straight-haired boy
Style direct et indirect
Style indirect vers style direct
- Liz asks what time wilma arrives ---->
Liz : " What time does Wilma arrives ? "
- Mrs Lee said she was worried ---->
Mrs Lee : " I am worried "
- The campers asked Jack if could help them
----> The campers : " Can you help us "
- Liz says her boyfriend is nice ----> Liz
: " My boyfriend is nice
- My English teacher asked my parents if they
were worried ----> Are you worried ?
- The weatherman said it was going to rain
----> It is going to rain
- She said she couldn't come because she was
too tired ----> I can't come because I am too tired
Style direct vers style indirect
- Liz " I swim everyday " ---->
Liz says she swims every days
- Liz to Jack : " Can you help me ? ---->
Liz asks Jack if he can help her
Qualities and defects

Qualities :
- Sociable
- good-tempered, cheerful : gai, heureux, bon
caractère
- brave : courageux
- tidy = ordely
- organized
- reponsible
- generous
Defects
- lazy : parreseux
- greedy : gourmand
- untidy = disorderly = messy
- timid : peureux, timoré
- selfish : égoiste
- bad-tempered = moody = grumpy : grognon /
ronchon
Capacité et fréquence
Le niveau de savoir-faire
- Question : Hoor well can you swim ?
- Réponse : ( *** ) I can swim very
well / ( ** ) I can swim quite / ( * ) I can swim a little / ( ) I can't swim
at all
La fréquence
- Question : How often do you swim ?
- Réponse : ( ** ) often / ( ** ) sometime / ( ) never
 L'
adverbe de fréquence se place entre le sujet et le verbe
L'
adverbe de fréquence se place entre le sujet et le verbe
Exercice de capacité
et de fréquence
- Sais-tu faire un gateau au chocolat
? Oui c'est facile ! ----> Can you make
a chocolate cake ? Yes I can it's easy
- Est-ce que tu sais bien cuisiner ? Non, je ne sais
pas du tout ----> How well can you cook
? No, I can't cook at all
- Est-ce que ton frère sait bien skier ? Oui,
il sait faire un peu ----> How well can
your brother ski ? Yes, he can ski little
- Est-ce que tu vas souvent à la piscine ?
----> How often go to the swimming pool
( once a week )
- Est-ce que tes parents vont souvent au restaurant
? How often do your parents go to the restaurant
?
- Non ils n'y vont jamais ---->
No, they never go to the restaurant
|
Wake up !
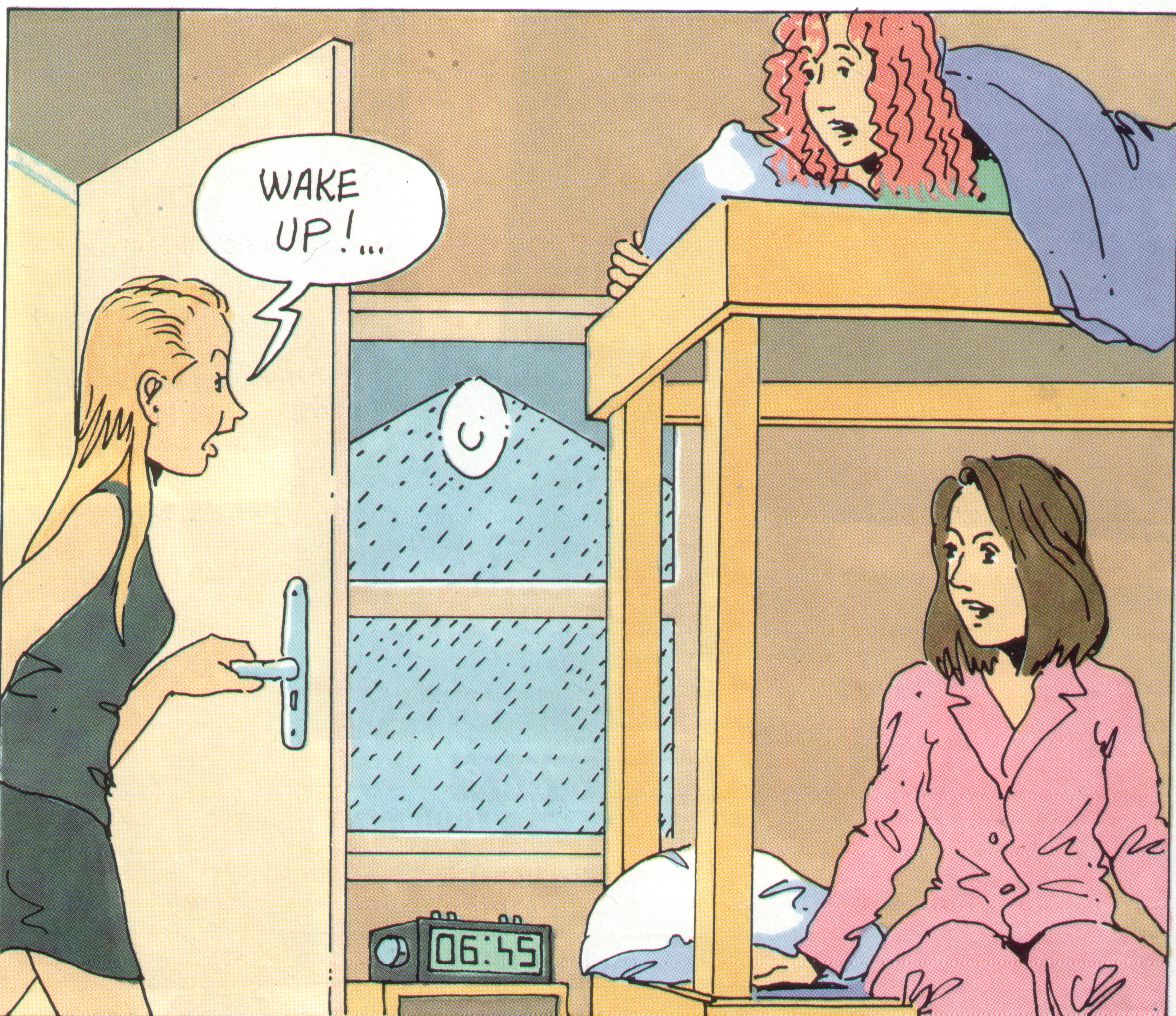

- 6 h 45 : it is quarter to seven
- The scene take place in Wilma and Deb's bedroom
- What's the weather like ? It's raining
- Deb in a bad mood because it is too early to get up
- She can't beer jogging in the rain
- Leave me alone : Laisse moi seule
- Are you joking : Tu plaisantes ?
- What time is it ?
- 16 h 30 : half past seven
- 17 h 15 : quater past seven
- 22 h 10 : ten past ten
- 17 h 45 : quarter to height
- 18 h 55 : five to nive
- 08 h 00 : height o' clock
Wake up ( dialogue )
Wilma : Deb ! where are you ? It was fabulous.
We ran along the beach.
Deb : I'm in the bathroom. I'm washing my hair.
Wilma : At half past seven in the morning ?
Deb : Yes, I wash my hair every morning before
breakfast.
Wilma : Well, hurry up ! I'm wet.
Deb : So am I !
Wilma : What are you doing, Deb ? You' ve been
in there for hoors.
Deb : I' m drying my hair
( the door opens )
Liz : Well girls, after breakfast there are some
chores to do. You can choose between potato peeling, cleaning or washing up.
Which would you prefer, Wilma ?
Wilma : I don't mind cleaning but I can't bear
washing up.
Liz : Good. Wilma for cleaning. What about Deb
?
Wilma : Put her down for washing up. I'm sure
she won't mind.
Deb : The bathroom is yours. What did liz want
?
Wilma : Nothing much. She wants tou to do the
washing-up after brakfast, that's all
Deb : What ?
- To peel ----> I hate peeling the potatoes !
- chores : les corvés
- wet / dry : mouillé / sec
- to dry : Deb is drying her hair
- I don't mind : ca m'est égal
La proposition infinitive
|
Want |
|
me |
|
|
|
Ask |
|
you |
|
|
|
would like |
|
him |
|
|
| SUJET + |
tell |
+ pronom complément |
her |
+ to |
+ verbe |
|
|
|
us |
|
|
|
|
|
them |
|
|
Exemples :
- I want you to come : je veux que tu viennes.
- He asked her to do the washing up : il lui a demandée
de faire la vaisselle.
- They would like me to organise the party : ils aimeraient
que j'organise la soirée
- I told him not to phone everyday. Je lui ai dit de ne pas
téléphoner tous les jours
Exercices :
- Elle m'a demandé de rester : She
asked me to stay
- Il lui a dit de téléphoner au médecin
( lui = sa fille ) : he told her to phone the doctor
- Nous aimerions que tu apprennes l' italien : We
would like you to learn italian
- Ils veulent qu'il soit le premier : They
want him to be the first
- Paul asked me to help him : Paul
: " Help me "
- Paul told Mary to come at twelve : Paul
: " Come at twelve "
- Paul asked his Mum to drive him to school
: Paul : " Drive me to school "
- Mrs Baker wants her children to make their
beds : Mrs Baker : " Make your bed "
Morning routines and after
/ before

Liz is a champion !

Verbs
- to practise = to train ----> Liz practises for 6 hours
everyday
- to manage : réussir à
- to laugh ( rire au éclats ) > to smile ( rire )
- to reply = to answer : répondre
Vocabulary
- health / healthy ----> Liz must lead a healthy life
- whether = if
- the movies = the cinema
|
Exercice : Utilisez can / can't / mustn
't / should / shouldn't
- My brother can't read
: he is 2 years old !
- If you want to lose 3 kilos, you should
do exercises everyday and you shouldn't
drink sweet drinks
- You are un bad health. You must
stop smoking
- Look at her ! she's drinking a glass of whiski ! she
musn't drink whisky !
- It is forbidden. You mustn't
smoke here
- Liz can swim for 3 hours.
- You look tired, I think you should
go to bed earlier.
|
|
Utilisez too much ( trop
de chose que l'on peut compter ) / too many ( trop de choses que l'on
ne peut pas compter ) / so much ( autant de choses que l'on peut compter
) / so many ( autant de de chose que l'on peut pas compter ) / enought
( pas assez de )
- He eats too
much
- He eats too
much sugar and to many crisps
- He doesn't drink enough
water
- He doesn't do enought
exercises
- He shouldn't watch too
much television
- He shouldn't eat so
many cheese
- He shouldn't drink so
much coke
- He shouldn't eat
so many chocolate bars
- He shouldn't spend so
much time on the sofa !
- He doesn't eat enough
french beans
|
They made a history ( the
simple past )


|
To be
|
|
I was
|
|
you were
|
|
he / she was
|
|
we were
|
|
you were
|
|
they were
|
When did he die ?
Beethoven ? He died in 1827
How many children did he have ?
He had 4 childrens
Dans les questions avec to be, on inverse le sujet et l'auxiliaire
être ----> Where were you yesterday
Dans les questions avec un verbe lexical, on utilise l'auxiliaire
did ----> What did Christopher Columbus do ? He discovered America /
What did Victor Hugo write ? He wrote " les misérables "
Questions sur la dâte et le lieu de naissance ---->
When / Where was he born
Questions sur la date et le lieu de décès
----> When / Where did he die ?

Wilma's letter


Vocabulary :
- roommate = Wand Deb are roommates = they sleep in the same
bedroom
- a " wet blanket " = Deb is a wet blanket = She
is always grumpy : rabat-joie
- muddy = Wilma's boot were muddy because she walked in the
country and it was raining
Verbs :
- to beat - beat - beaten : battre
- Wilma won the match = Deb was beaten
The Making of a Champion
.jpg)

Verbs :
- qui désigne une présence ou
une absence : There are 21 pupils in the class room
- qui désigne un temps écoulé
entre 1 évènement passé daté et le présent
---> prétérit : Liz joined the national team 10 years ago
Vocabulary :
- the headline : the title
- her youth = when she was young
- to drop : laisser tomber ( dropped )
- to be thrilled = to be very happy
- Paul was disappointed because Liz only saw
hotels in Australia
Comparatifs et Superlatifs
Révision des comparatifs :
1 ) large :

n° 2 is larger than n°1
2 ) Comfortable :
n° 2 is more comfortable than n°1 / n° 1 is
less comfortable than n°2
3 ) messy ----> messier than / clever : 2 syllabes sans
" y " donc more clever than
4 ) Irréguliers
good ----> better than
bad ----> worse than
Les superlatifs :
- Formation :
- En anglais, l'adjectif épihète
se place avant le nom qu'il qualifie ----> Un pays froid : a cold country
/ La saison la plus froide : the coldest season
- Dire en anglais :
- L' exercice le plus facile : The
easiest homework
- L' exercice le plus dificile : The
hardest exercice
- La matière la plus interessante
: The most interesting subject
- La personne la plus mince : The
slimmest person
- La saison la plus chaude : The
hottest season
|
- Emploi de in ou de of après un superlatif
:
- Tu as remarqué qu' en anglais on
dit :
- John is the tallest boy in the class (
= de notre classe : un groupe humain )
- Is Tokyo the biggest city in the world ? ( = du monde :
lieu )
- Mais : Spring is the nicest season of the year ( = de l'année
: notion de temps )
- Dis en anglais
- La personne la plus agée de ma famille a
98 ans : The oldest person in my faliky is
98
- La montagne la plus haute d' Ecosse est le Ben
Nevis : The tallest mountains in Scotland
is Ben Nevis
- Je ne sais pas qui est le meilleur acteur de l'année
: I don't know who is the best actor of the
year
- Le romancier le plus célèbre de sib
siècle est Victor Hugo :The most famous
writer of the century is Victor Hugo
|
Present Perfect

Vocabulary :
- Mrs Taylor is cross = angry = furious because the boys haven't
cleaned
- The bath and they haven't hoovered under the bed
- They haven't changed the sheets
- She doesn't understand why there is an alarm-clock, a pair
of socks and a backpack under the bed
- Walter has hidden Deb's bag and alarm-clock ( to hide / hid
/ hidden : cacher )
- He has played a trick on Deb : Il a joué un mauvais
tour à Deb
- Deb is going to take a revenge : se venger

Formation
- Le present perfect est formé de
has / have + le participe passé
- Le participe passé des verbes réguliers
----> ed
- Pour les verbes irréguliers ---->
3e collone des verbes irréguliers
Utilisation
- On utilise le present perfect pour faire
le bilan d' une action qui vient juste de se produire
YER and STILL
- Yet se met toujours à la fin de la
proposition
- Walter hasn"t cleaned the bath yet ----> pas
encore...
- He still hasn't cleaned the bath ---->il n'a toujours
pas...
Le present perfect avec ever / already / never
- Have you ever been to Rome ? ---->
Est tu déja allé à Rome ?
- Yes, I have already been to Rome ---->
Oui, je suis déja allé à Rome
- No, I have never been to Rome ---->
Non, je ne suis jamais allé
Le superlatif et le présent perfect
- My computer is the most beautiful present I have eve received
( que j'ai jamais recu )
- " Titanic " is the most romantic film I have ever
seen ( que j'ai jamis vu )
- Conclusion : Dans une phrase afformative contenant un superlatif,
je dois utiliser ever
Le présent perfect et les élèments
datés
- Lorsque l'action passé est datée,
je dois utiliser le simple past
- She went to pain in 1996
- I visited Paris two years ago
- I bought this car last june
- Lorsque qui n'y a aucune information sur
le moment : Mrs Taylor has been to Spain, I've bought a new car
Moi aussi / moi non plus
" I have visited Munich " ----> So have I
" I have never seen this man " ----> Neither
have I

The green code


- Picture a : the boy mustn't walk in the field, he should
walf on a path
- Picture e : he shouldn't brush his teeth in the water tank
- Picture d : he needn't carry his dog
| MUST |
obligation |
| MUSTN'T |
interdiction |
| SHOULD |
conseil |
| SHOULDN'T |
reproche |
| NEEDN'T |
absence de necéssité |
Les 6 façons de dire une interdiction
- Don't pak the car
- You musn't pak the car
- It is forbiden to park the car
- It is not allowed to park the park
- Parking the car is not allowed
- Parking the car is forbidden
The hike
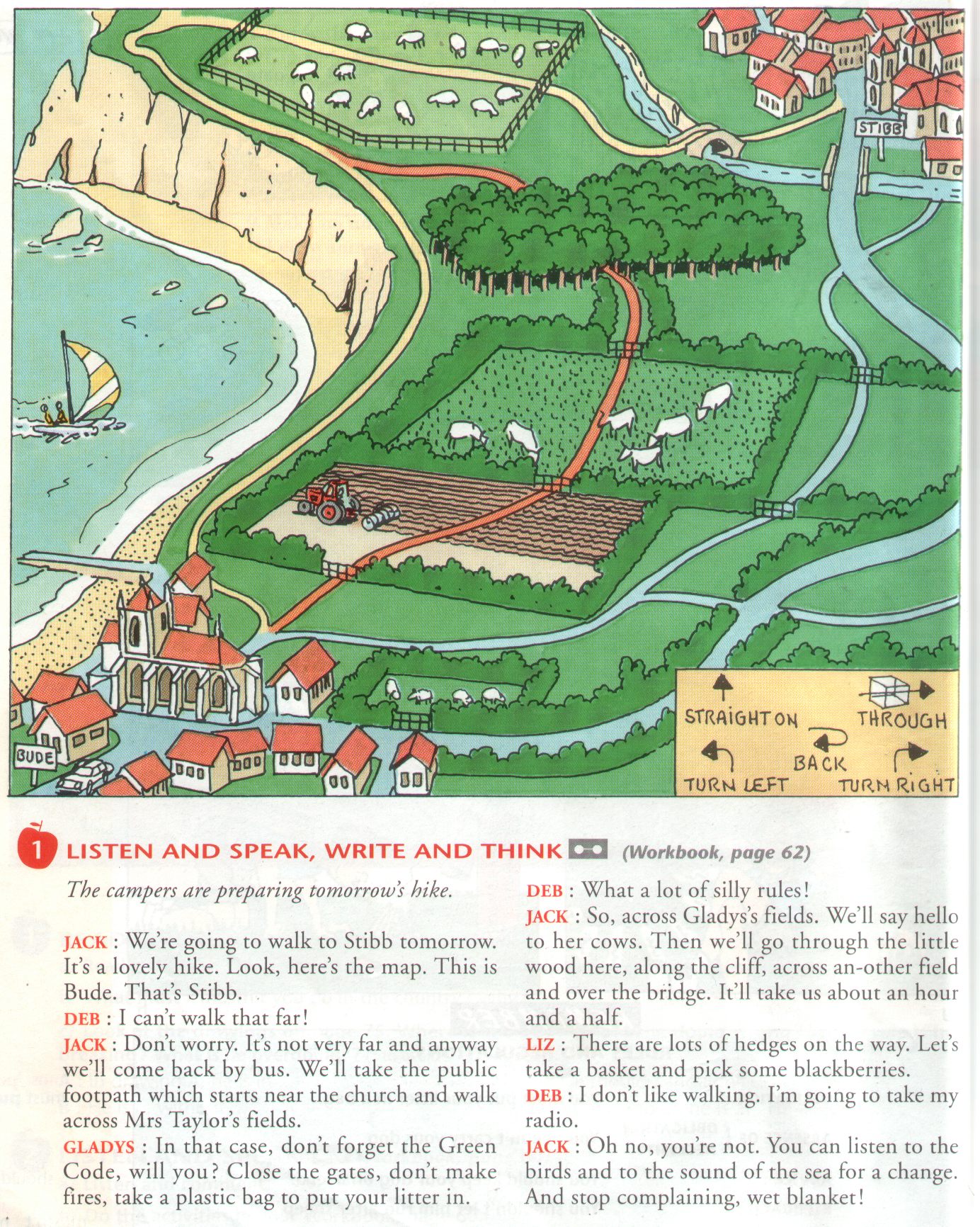
Vocabulary
- far / near : loin / proche
- blackberried : les mures
- 1 h et demi : one hour and a half
- 1 demi heure : half an hoor
Verbs
To walk across the fields / the street ( passer à
travers / traverser )
To walk trough the wood ( marcher à
travers la forêt
To go along the river ( marcher à coté de la rivière
)

To go over the bridge ( passer sur le pont
The glady's farm


Vocabulary
- peas : petits pois
- french beans : haricots verts
- Gladys collects the eggs every morning
- Mr Taylor milks the cows twice a day
Verbs
- to grow-grew-grown : pousser
- to feed-fed-fet : donner à manger
Grammar
- MUST = HAVE TO / HAS TO : have to s'utilise
pour les obligations de la vie ----> Mr Taylor has to milk the cows / We
have to listen to her teacher
Expressions
- You're pulling our leg ! : Tu nous fait marcher
/ Tu te moques de nous
Have to

Exercice :
- Un fermier doit traire ses vaches
deux fois par jour : ---> obligation --->
présent ---> A farmer has to milk his cows twice a day
- Nous ne sommes pas obligés
de longer la falaise : ---> Absence d'obligation
---> présent ---> We don't have to go along the cliff
- Ils ont du traverser les champs de
Mrs Taylor : --->obligation ---> passé
---> They had to walk across Mrs Taylor's fields
- Il faudra que tu nourrisses les poules
---> obligations ---> futur ---> You
will have to feed the chikens
- Nous n'avons pas eu le droit d'utiliser
le portable de Gladys ---> interdiction --->
passé ---> We weren't allowed to use Gladys's portable
- Ils ont pu organiser une fête
pour l' anniversaire de Liz : Mrs Taylor a accepté --->
Autorisation ---> passé ---> They were allowed to organize
a party for Liz's bithday, she accepted
- Tu ne seras pas obligé de
venir avec nous ---> absence d'obligation
---> futur ---> you won't have to come with us
|
The picinic

Vocabulary :
- salt : sel
- pepper : poivre
- hard(boiled egges : oeufs durs
- crisps : chips
- ants : les fourmis
- bees : les abeilles
- spiders : arraignés
- sunny : ensoleilé
- the wind / it is windy : le vent
- grown-ups : adultes
- to fish : pecher
- to hope : esperer / souhaiter
- I am afraid of : j'ai peur de ..
GRAMMAR :
- CAN n' existe qu'au présent et au
passé ( could ) alors, au futur on le remplace par be able to --->
the campers will be able to swim ( pouron nager ) / the campers won't be able
to fly a kite ( ne pourront pas )
MAY : c'est une auxiliaire de modalité comme can et
must qui est invariable. Il exprime la probabilité ----> the weather
may be nice this afternoon / they may catch fish
SHAL : c'est un auxiliaire de modalité qui permet de
suggérer ---> Shal we go to the cinéma ? ( Et si on allait
au cinéma )
Le present perfect avec for
et since

Conclusion : for est utilisé
pour introduire la durée alors que since introduit le point de
départ
- How long have you lived in St Jean de
Braye ? I have lived in St Jean de Braye for 5 years
- How long did you live in Marigny ? I
lived in Marigny for 2 years
Exercice FOR / SINCE / AGO
- Nous apprenons l'anglais depuis
3 ans : We have learn't English for 3 years
- Nous apprenons l'anglais depuis
1997 : We have learn't English since 1997
- Mon grand-père a appris
l' anglais pendant 4 ans : My grand father
learn't English for 4 years
- Je suis allé au restaurant
il y a 3 jours : I went to restaurant 3 days
ago
- Il n'a pas été malade
depuis plusieurs années : He haven't
been ill for a few years
- Il a été malade il
y a 2 mois : He was ill 2 month ago
- L' été dernier, il
a été malade pendant 6 semaines : Last
summer. He was ill for 6 weeks
- Il est malade depuis dimanche :
He has been ill since sunday
- Depuis combien de temps travaille-t
- il dans cette banque ? Il y travaille depuis la fin de la guerre
: How long has he worked in this bank ? He
has worked since the enf of the war.
- Il y a combien de temps que tu
as acheté ta voiture ? Je l'ai achetée il y a 3 ans.
How long ago did you bought your car ? I baught
it 3 years ago
|
L'
adverbe de fréquence se place entre le sujet et le verbe

.jpg)